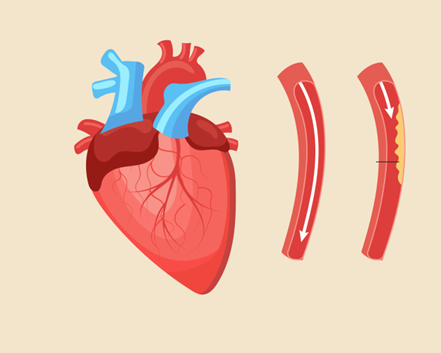
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) is a widespread cardiovascular condition affecting millions globally. This article offers a concise overview of CAD, focusing on its symptoms, causes, and available treatment options.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease:
Common symptoms of CAD include:
- Chest pain or discomfort, known as angina
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Sweating
- Pain that may radiate to the arm, jaw, or back
These symptoms often indicate reduced blood flow to the heart, signaling the presence of CAD.
Causes and Risk Factors:
CAD develops primarily due to the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which is responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart. Plaque consists of cholesterol, fat, calcium, and other substances. This buildup narrows the arteries and restricts blood flow to the heart. Key risk factors for CAD include:
- High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels contribute to plaque formation.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure increases arterial wall stress, promoting plaque accumulation.
- Smoking: Chemicals in tobacco damage blood vessels, accelerating plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can harm blood vessels, heightening the risk of CAD.
- Obesity: Excess weight strains the heart.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to poor cardiovascular health.
- Family History: Genetic predisposition can increase susceptibility to CAD.
- Age: The risk of CAD rises with age.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for CAD focuses on managing symptoms and reducing the risk of further complications. Options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: A heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management can slow or even reverse CAD progression.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe statins to lower cholesterol, blood pressure medications, and aspirin to prevent blood clots.
- Medical Procedures: For severe CAD, procedures like angioplasty and stenting or bypass surgery may be necessary. Angioplasty uses a catheter with a balloon to widen narrowed arteries, while stenting keeps the artery open. Bypass surgery involves using healthy blood vessels from other parts of the body to reroute blood flow around blocked arteries.
Coronary Artery Disease is a serious health concern with potentially life-threatening consequences. Recognizing symptoms, understanding causes, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps in managing CAD. Early detection and lifestyle changes play a vital role in preventing and managing this condition, helping individuals protect their cardiovascular health.